Introduction to the Modular Blockchain: What is it and how does it work?

Welcome to the web3 tech series - This newsletter will delve into both our core tech stack and the latest developments in the web3 ecosystem, published every Friday. In our second edition, we'll deep dive into the concept of a modular blockchain and how Morph has integrated a modular design.
Let’s dive into it.
TL;DR: What is a Modular Blockchain?
At its core, a modular blockchain is an architectural framework that segments some of the functionalities of a blockchain network into distinct modules or components. Each module specializes in a particular function, such as consensus, data storage, or transaction execution, operating independently yet cohesively within the broader ecosystem. This compartmentalization stands in stark contrast to traditional monolithic designs, where all operations are tightly integrated into a single, indivisible system. Modular blockchains champion the principles of flexibility, scalability, and upgradability, providing a solid foundation for building complex, efficient, and adaptable digital infrastructures.
Monolithic vs. Modular
The distinction between monolithic and modular blockchains is analogous to the difference between a Swiss Army knife and a specialized toolkit. While a Swiss Army knife offers convenience with its all-in-one design, a toolkit boasts specialized tools that deliver superior performance for specific tasks. Monolithic blockchains, akin to the Swiss Army knife, integrate all functionalities into a single framework, which can simplify deployment but often at the expense of efficiency and flexibility. Modular blockchains, on the other hand, resemble a toolkit, where each tool (module) is optimized for its intended function, resulting in enhanced performance, easier upgrades, and greater adaptability to changing requirements.
How Does a Modular Blockchain Work? The Technical Architecture
The essence of a modular blockchain lies in its division of labor; it deconstructs the traditional blockchain stack into separate layers or modules, each responsible for a distinct aspect of the blockchain's functionality. This section explores the technical architecture of modular blockchains, breaking down the components and illustrating how they work together to create a more efficient and flexible blockchain ecosystem.
Core Components of a Modular Blockchain
1. Consensus Layer: This foundational layer is responsible for achieving agreement on the state of the blockchain among all participants. Unlike monolithic blockchains, where consensus is tightly coupled with other operations, modular blockchains allow for the consensus mechanism to be an independent module. This separation enables the use of different consensus algorithms depending on specific network requirements, enhancing security and efficiency.
2. Execution Layer: The execution layer handles the processing of transactions and smart contracts. By isolating this functionality, modular blockchains can optimize transaction throughput and smart contract execution, reduce costs, and improve scalability. Developers can choose execution environments that best suit their application's needs, from simple payment transactions to complex decentralized applications.
3. Data Availability Layer: This layer ensures that all necessary data for validating transactions and smart contracts is readily available to network participants. It addresses one of the scalability challenges in blockchain by allowing data to be stored off-chain or on specialized data shards, significantly reducing the burden on the main network while ensuring integrity and accessibility.
4. Settlement Layer: The settlement layer is where the finality of transactions is recorded. It serves as the ultimate ledger, providing security and durability to the blockchain. In a modular architecture, this layer can leverage the strengths of established blockchains, such as Ethereum, for secure settlement, while offloading other functionalities to more efficient modules.
5. Interoperability Layer: Essential for modular blockchains, this layer facilitates communication and interoperability between different blockchain modules and even between distinct blockchain ecosystems. It enables the seamless exchange of information and value, unlocking the potential for complex cross-chain interactions and applications.
How These Components Interact
The interaction between these components is orchestrated through well-defined interfaces and protocols, allowing each module to communicate and cooperate without needing to be aware of the inner workings of other modules. This design not only simplifies development and maintenance but also enhances the blockchain's overall performance by allowing each module to be optimized for its specific task.
For example, a transaction could be initiated in the execution layer, where it is processed and validated according to the smart contract logic. The result of this execution is then passed to the consensus layer, where network participants agree on the outcome. Once consensus is achieved, the transaction data is made available through the data availability layer, and the final state is recorded in the settlement layer. Throughout this process, the interoperability layer ensures that all components can efficiently interact and exchange necessary information.
By structuring the blockchain into these discrete modules, developers have the flexibility to innovate within individual layers, swap out components as better solutions become available, and customize the blockchain infrastructure to fit the unique needs of different applications. This modular approach not only streamlines development and enhances performance but also fosters a more vibrant and diverse ecosystem of blockchain solutions.
How Morph Integrated Modular Design
Morph exemplifies the application of modular design principles within the Layer 2 (L2) solutions. By adopting a modular architecture, Morph offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing developers to tailor their apps by integrating only the necessary modules. This strategic approach not only optimizes performance by reducing complexity but also ensures that the platform can swiftly adapt to technological advancements without overhauling the entire system. Morph's dedication to modular design sets it apart from conventional L2 solutions, fostering an environment where developers can unleash their creativity to build more efficient, scalable, and innovative decentralized applications (dApps).
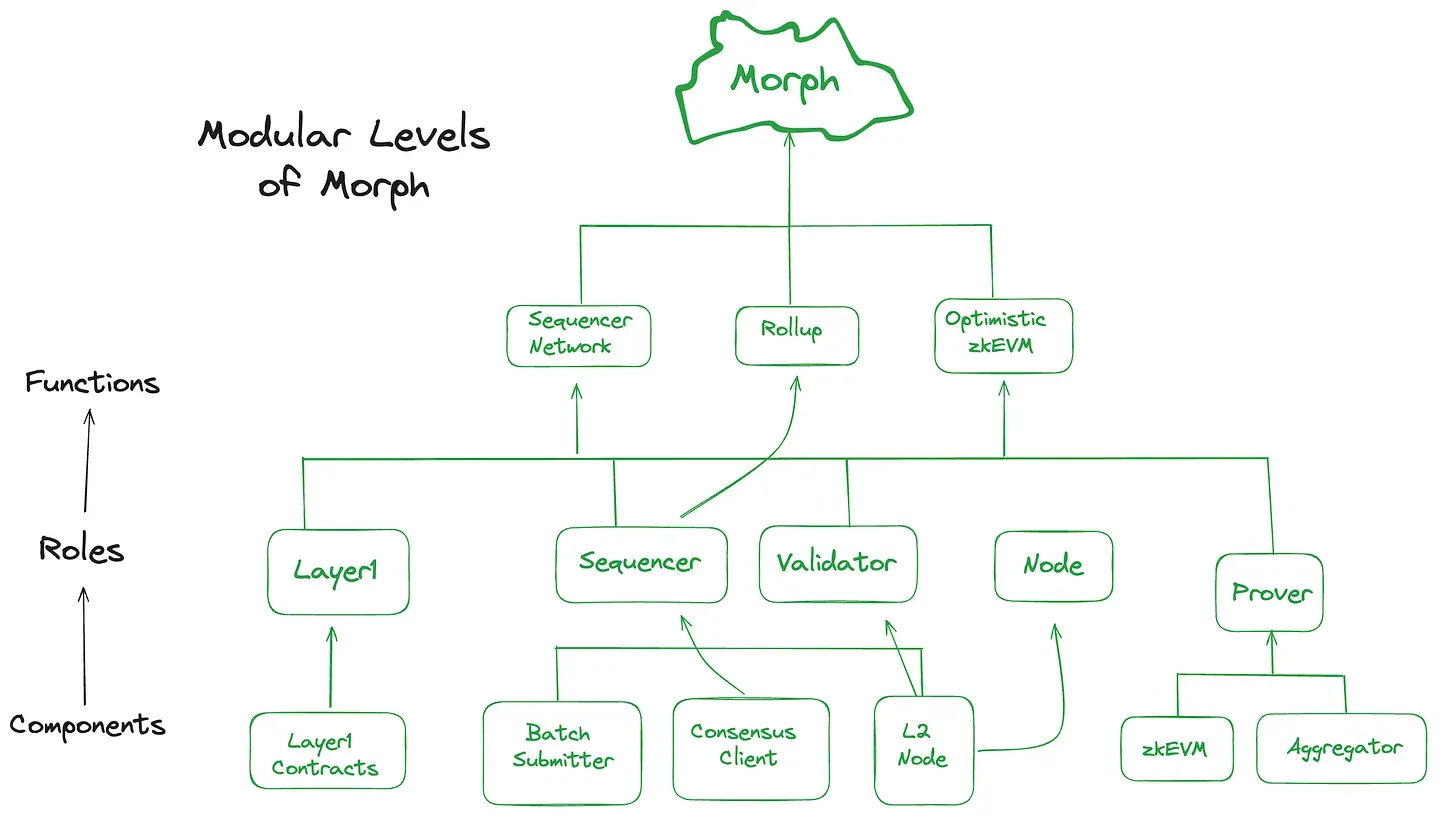
The Benefits of Modularism
- Enhanced Flexibility: Modular architectures enable rapid adaptation to new technologies and changing market demands, ensuring that blockchain platforms remain at the forefront of innovation.
- Scalability: By isolating specific functionalities into modules, blockchain networks can scale more efficiently, handling increasing loads without compromising performance.
- Ease of Upgrades: Upgrading or adding new features becomes significantly simpler in a modular system, as changes can be made to individual modules without disrupting the entire network.
- Customization: Modular blockchains offer a higher degree of customization, allowing developers to pick and choose the components that best fit their application's needs, leading to optimized solutions.
- Reduced Complexity: By decoupling the system's components, modular designs simplify the underlying architecture, making it easier to develop, maintain, and secure.
Conclusion: The Future is Modular
The transition towards modular blockchain architectures marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of blockchain. As we've seen with chains like Morph, the modular approach not only solves many of the challenges faced by monolithic systems but also opens up new avenues for creativity, efficiency, and scalability. By embracing modularism, the blockchain community is laying the groundwork for a future where digital infrastructures are more adaptable, resilient, and tailored to the diverse needs of users across the globe. As we continue to explore the vast potential of blockchain technology, the modular paradigm stands out as a beacon of innovation, guiding us toward a more flexible, scalable, and customizable digital future.
Wrapping it Up
Hopefully this guide has provided you the essential information to know more about our core tech stack. We encourage you to provide feedback and ask questions, and subscribe to our newsletter for future articles.
You can also join our discord channel or follow us on Twitter.





